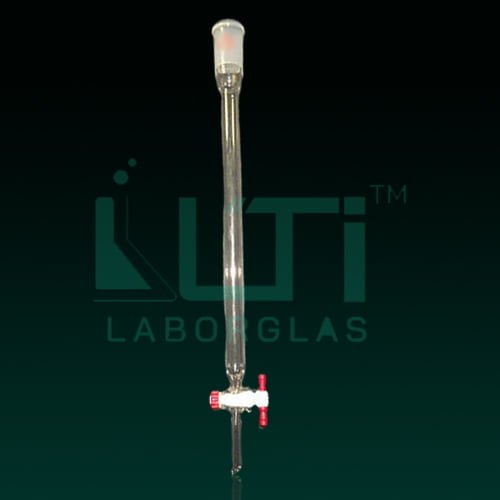
- Heavy wall Design
- General purpose column has a PTFE stopcock and a top outer joint for flash chromatography
| PART No. | Size (mm) | Female Joint | Bore (mm) | PACK Qty. |
| 5970-17 | 17 x 305 | 24/40 | 2 | 1 |
| 5970-32 | 32 x 457 | 24/40 | 2 | 1 |
Here are some common applications:
- Column Chromatography:
- Traditional column chromatography involves packing a column with a stationary phase and passing a mobile phase through it. Different compounds in the sample interact with the stationary phase at varying degrees, leading to separation.
- High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC):
- HPLC employs high-pressure pumps to pass liquid samples through a chromatography column at high speeds. It is a powerful analytical technique widely used for separating and quantifying components in a mixture.
- Gas Chromatography (GC):
- In GC, a gaseous sample is injected into a chromatography column where it interacts with a stationary phase, leading to separation based on factors such as volatility and affinity.
- Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC):
- SEC separates molecules based on their size as they pass through a gel-filled chromatography column. Larger molecules move more rapidly through the column, while smaller ones are impeded.
- Ion Exchange Chromatography (IEC):
- IEC separates ions based on their charge. Chromatography columns with ion-exchange resins facilitate this separation, allowing scientists to isolate and analyze ions in a sample.
- Affinity Chromatography:
- This technique uses specific interactions, such as antigen-antibody binding, to separate and purify biomolecules. Chromatography columns with affinity resins selectively capture the target molecules.
- Reverse Phase Chromatography:
- In reverse phase chromatography, the stationary phase is nonpolar, leading to the separation of compounds based on their hydrophobic interactions. This is commonly used in HPLC.
- Flash Chromatography:
- Flash chromatography is a rapid form of chromatography used for quick separations. It employs chromatography columns with larger diameters to achieve faster flow rates.
- Purification of Chemical Compounds:
- Chromatography columns are widely used for the purification of chemical compounds, removing impurities and obtaining high-purity substances for various applications.
- Protein Purification:
- Chromatography columns are extensively used in protein purification processes. Techniques such as size exclusion chromatography and affinity chromatography help isolate proteins with high purity.
- Environmental Analysis:
- Chromatography columns are employed in environmental analysis to separate and quantify pollutants, contaminants, or components in environmental samples.
- Food and Beverage Analysis:
- Chromatography is used to analyze food and beverage samples for quality control, identifying additives, flavor compounds, and contaminants.
- Drug Development and Pharmaceutical Analysis:
- In pharmaceutical research and development, chromatography columns are used to separate and analyze drug compounds, ensuring their purity and efficacy.
- Educational Purposes:
- Chromatography columns are valuable teaching tools in academic settings, allowing students to learn and practice separation techniques in chemistry and biology labs.
- Biotechnology and Biomedical Research:
- Chromatography columns play a crucial role in various biotechnological processes, including the separation and purification of biomolecules for research and therapeutic purposes.