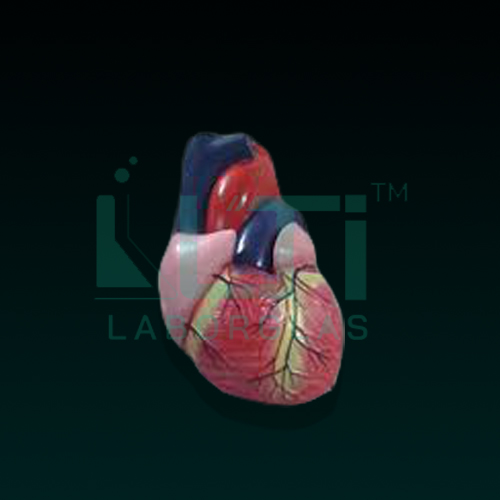
Here are seven common parts found in such models, along with their educational uses:
- Base and Apex:
- Use: Understanding the External Anatomy
- Purpose: The base and apex components help identify the external features of the heart. Students and healthcare professionals can learn to recognize the base, which is where major blood vessels attach, and the apex, the pointed end of the heart.
- Atria (Left and Right Atrium):
- Use: Understanding Heart Chambers
- Purpose: Atria are the upper chambers of the heart responsible for receiving blood. Models with separate left and right atria allow students to study their structure and function in detail.
- Ventricles (Left and Right Ventricle):
- Use: Studying Heart Chambers and Pumping Action
- Purpose: The ventricles are the lower chambers that pump blood out of the heart. Separate left and right ventricles on the model help illustrate their role in pumping oxygenated and deoxygenated blood to the body.
- Aortic and Pulmonary Valves:
- Use: Learning about Heart Valves
- Purpose: Models often include aortic and pulmonary valves, which help demonstrate the one-way flow of blood out of the heart. This aids in understanding the cardiac cycle and valve function.
- Tricuspid and Bicuspid (Mitral) Valves:
- Use: Detailed Valve Study
- Purpose: Tricuspid and bicuspid (mitral) valves are located between the atria and ventricles. Models with these valves separated allow for a more detailed examination of their structure and function.
- Pulmonary Artery and Aorta:
- Use: Studying Major Blood Vessels
- Purpose: The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs, while the aorta carries oxygenated blood to the rest of the body. Models with these vessels help illustrate the pathways of blood circulation.
- Vena Cava (Superior and Inferior):
- Use: Understanding Blood Return to the Heart
- Purpose: The superior and inferior vena cava are major veins that return deoxygenated blood to the right atrium. Models including these vessels aid in understanding the venous return to the heart.
Educational Uses:
- Anatomy and Physiology Courses: These models are commonly used in anatomy and physiology classes to teach students about the structure and function of the heart.
- Medical Training: Healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, and paramedics, use these models for training in cardiac anatomy and understanding heart function.
- Patient Education: Healthcare providers use heart models to explain heart conditions, surgeries, and procedures to patients.
- Research: Heart models may be used in research settings to visually represent and study cardiac anatomy.