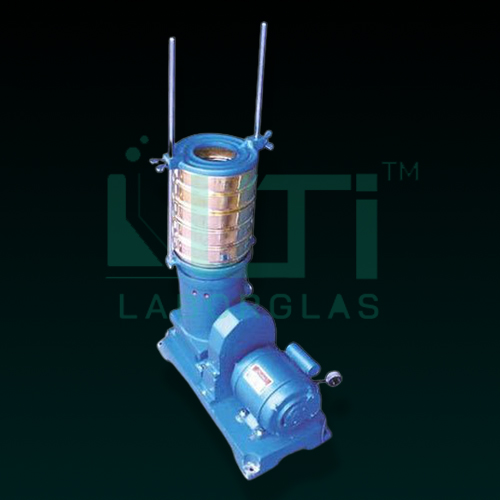
- SIEVE SHAKER (GYRATORY TYPE) driven by a 0.25 H.P. motor, 220 volt A.C. through a reduction gear and is suitable to carry upto 7 sieves of 12” or 8″ dia.
- When clamped the sieve table does not rotate but is inclined from the vertical axis and the direction of inclination changes progressively in the clockwise direction.
- In addition to the gyratory motion of the shaker there is an upward and downward movement at a frequency of 270 r.p.m.
- The whole mechanism runs in oil bath and the table can be unclamped to give an additional rotary motion.
- Analog Timer 0-60mins is inbuilt in the shaker.
A sieve shaker with gyratory motion serves various purposes in short form:
- Particle Size Analysis:
- Determine the particle size distribution of granular materials for quality control and research.
- Quality Assurance in Construction:
- Ensure the uniformity of construction materials like aggregates through particle size testing.
- Soil Analysis:
- Analyze soil samples to understand their composition and classify them based on particle size.
- Pharmaceutical Granule Sizing:
- Assess the particle size of pharmaceutical granules for quality control in drug manufacturing.
- Food Industry Quality Control:
- Monitor and maintain the consistency of particle size in food processing for quality assurance.
- Chemical Processing:
- Optimize chemical processes by analyzing and controlling the particle size of powders and granules.
- Mining and Minerals:
- Evaluate the particle size distribution of minerals and ores for efficient processing.
- Environmental Testing:
- Determine the particle size distribution in environmental samples to study sedimentation patterns.
- Research and Development:
- Aid in various research applications where particle size analysis is crucial for experimentation.
- Powder Characterization:
- Characterize powders used in industries like cosmetics, ceramics, and powder metallurgy.
- Pharmaceutical Formulation:
- Support pharmaceutical formulation by ensuring the appropriate particle size of active ingredients.
- Cement Industry:
- Monitor and control the particle size of cement materials for quality in the construction industry.